
As you may know, here at Real Pickles we are deeply committed to buying our vegetables only from Northeast family farms and selling our products only within the Northeast. One way in which we are able to achieve this, and in turn help to build a strong, organic and regional food system, is by working with small independently-owned regional distributors who bring Real Pickles to our Northeast neighbors.

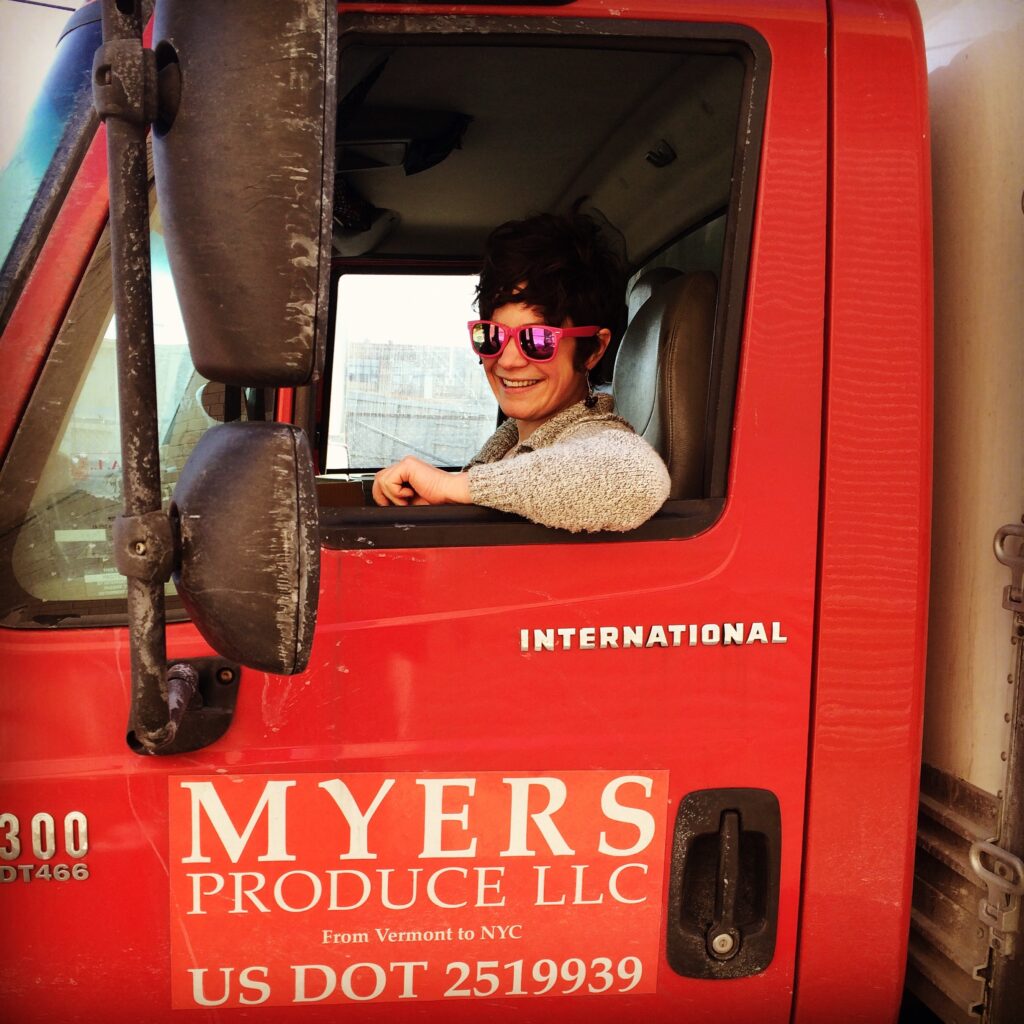
With this in mind, we began partnering with Myers Produce in 2016 as a way to bring our ferments deeper into the urban areas of the Northeast, and we’ve been thrilled with the results!
Myers Produce has been in operation since 2013. As a regional distributor based in Vermont, they buy vegetables and value added foods primarily from small, mostly organic farms in Vermont, Massachusetts and Maine. They then truck and sell to stores and restaurants in the New York City and Boston areas. Everything they offer has been produced in the Northeast. It’s a beautifully closed loop!
I recently chatted with Annie Myers, owner and founder of Myers Produce, about her experience delivering delicious regionally-grown food to cities in the Northeast. Read about it here, and let us know your thoughts on how regional food fits into your life.
How did you decide to start a food distribution business?
AM: I had been working on a farm in Northern Vermont for about three years at the time, and it had become clear that the farms in my area were struggling to reach markets outside the state. After the local wholesale market was maxed out, our farm considered major supermarket chains to be the best option for increased sales, and the demands of those large supermarket chains were not well-suited to the structure and diversity of our vegetable farm. Although I had been living in Vermont, I am originally from Brooklyn, and had spent some time working in the food industry in New York. I had friends in the city who I knew were looking for a better way to source food grown in our region, and who could afford to pay reasonable prices for that food. After a few years of seeing the disconnect between Vermont farms and high-end urban wholesale customers, I decided to start a business that might connect the supply in Vermont with the demand in the city.
Who are your main customers?
AM: Our produce goes to retail stores and restaurants throughout NYC and the Boston area. Our largest customers are a food co-op, an online retailer, and a fast casual restaurant chain, all in NYC.
 How many truckloads of regionally-produced food do you deliver to New York City & Boston each year?
How many truckloads of regionally-produced food do you deliver to New York City & Boston each year?
AM: We deliver in NYC four times per week throughout the summer and three times per week throughout the year. We deliver to the Boston area five times per week through the summer and twice per week throughout the year. All told this is about 330 truck loads per year!
How has Myers Produce changed over the years since you started?
AM: When we started, the business consisted of me, a van, and a computer, and I was delivering exclusively to NYC customers once a week. We have grown a lot since then! We are now a team of ten employees operating four box trucks. Our mission has remained the same since the beginning – we work to increase Northeast farmers’ access to regional urban wholesale customers, in order to support the strength of agriculture and the regional food system in the Northeast.
How does the seasonality of our Northeast agriculture impact your business?
AM: We have a much less diverse list in the winter than we do in the summertime. We don’t source any products from outside the region, so as soon as a product goes out of season in the Northeast, it is no longer offered on our list. That said, many of our farmers do an amazing job of season extension, and our winter offerings are probably more diverse than you might expect! We have greenhouse-grown spinach, tomatoes, and cherry tomatoes year-round, and we generally have kale, fennel and leeks well into January. And we have added value goods made with locally-grown produce available as well, like products from Real Pickles!
In a relatively short period of time, you have built up a great reputation as a regional distributor. What are the integral aspects to your success?
AM: We don’t know the answer to this entirely, but I think we have prioritized efficient systems, clear communication, and good customer service from the very beginning. I know these things mean a lot to our farmers and producers, and to our urban customers.
 With all the farms and food producers in Vermont and the Pioneer Valley, how do you choose your offerings?
With all the farms and food producers in Vermont and the Pioneer Valley, how do you choose your offerings?
AM: We don’t have an exact formula, but we try to keep our list diverse and to offer a consistent high quality. We try to source the products that we consider to match growers’ strengths, while also balancing location, price point, seasonality, and scale.
What do we need to be thinking about as consumers and shoppers, in terms of building a strong regional food system?
AM: I know that all of our customers are constantly competing with huge corporate sources of food (Amazon/Whole Foods in particular), and that they are challenged to differentiate themselves in the eyes of consumers. I think the most important thing is for shoppers to be intentional about where they spend their money, and think about who they are supporting by where they buy their food. If we want to support local growers in the Northeast, we need to make sure to spend money where it will stay in regional circulation.
What is the most interesting behind-the-scenes aspect of Myers?
AM: We really only have one physical warehouse space. But, to cover the distances we cover while adhering to regulations – and also create jobs that we think are sustainable – we have drivers based in NYC, Western MA, and VT. All of these drivers start and end their days in the same locations, but they drive from VT to Western MA and back, from Western MA to NJ and back, from Western MA to VT and back, and from Western MA to Boston and back.
What has been your favorite aspect of your job over the years?
AM: I have always loved puzzles, and I’ve grown to enjoy creating systems that are physical, flexible, efficient, and full of moving parts. I love it when an opportunity or inquiry comes up on a given morning, and I get to think about how that opportunity fits into our current operation, send a few emails, make a few phone calls, and be able to take advantage of that opportunity (often by the next day) in a way that makes sense for all parties involved. It keeps me on my toes, and it helps me feel that Myers Produce is providing a real service that can adapt to the needs of the folks that we are trying to serve.









 These are essential questions for anyone who wants a better food system – one that is ecologically sound and socially just. After all, a big impetus for the rapidly growing movement to transform the food system is the modern-day reality that places like New England – quite capable of raising such crops as apples or tomatoes – will instead import them from thousands of miles away and burn up large quantities of climate-changing fossil fuels in the process.
These are essential questions for anyone who wants a better food system – one that is ecologically sound and socially just. After all, a big impetus for the rapidly growing movement to transform the food system is the modern-day reality that places like New England – quite capable of raising such crops as apples or tomatoes – will instead import them from thousands of miles away and burn up large quantities of climate-changing fossil fuels in the process.



 The change in Real Pickles’ ownership provides a number of collateral
The change in Real Pickles’ ownership provides a number of collateral









